The recent move by the US, Japan, and the Netherlands to impose chip export controls on China reflects the growing tensions between nations in the global marketplace. The semiconductor industry is one of the most important and lucrative in the world. In 2021, semiconductor sales reached 555.89 billion U.S. dollars worldwide with China being one of the largest producers. The global semiconductor industry is poised for a decade of growth and is projected to become a trillion-dollar industry by 2030. The US spearheading these sanctions with these allies has expressed concerns about China’s increasing dominance in the industry, leading to this latest move to try and curb their progress.
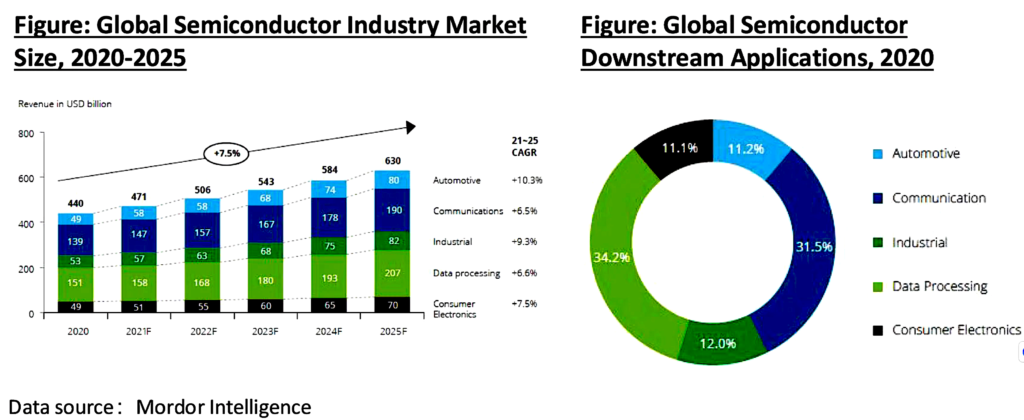
The recent move by the US, Japan, and the Netherlands to impose chip export controls on China reflects the growing tensions between nations in the global marketplace. The semiconductor industry is one of the most important and lucrative in the world. In 2021, semiconductor sales reached 555.89 billion U.S. dollars worldwide with China being one of the largest producers. The global semiconductor industry is poised for a decade of growth and is projected to become a trillion-dollar industry by 2030. The US spearheading these sanctions with these allies has expressed concerns about China’s increasing dominance in the industry, leading to this latest move to try and curb their progress.

I believe these export controls are aimed at slowing down China’s rapid rise in the semiconductor industry and ensuring that the US and its allies maintain their dominant position in the global marketplace. In justifying her position, the US has argued that China’s state-sponsored investments in the industry and its support of domestic companies are unfair practices that put foreign competitors at a disadvantage. It’s not surprising that technology has become a central issue in America’s concerns about China’s allegedly unfair and illegal economic practices.
The US government argues that Beijing’s substantial and undisclosed subsidies, which include preferential government financing and procurement contracts, have enabled Chinese tech companies like Huawei to gain a commanding presence in the market. The Chinese government’s discriminatory treatment of foreign firms in areas such as regulation, licensing, and market access has been a persistent issue, with American tech companies being the most likely to experience such discrimination. Additionally, China’s practices of coercing foreign companies into divulging trade secrets and intellectual property to their Chinese partners have had a disproportionate effect on US companies that rely on technology rights, knowledge, and data.
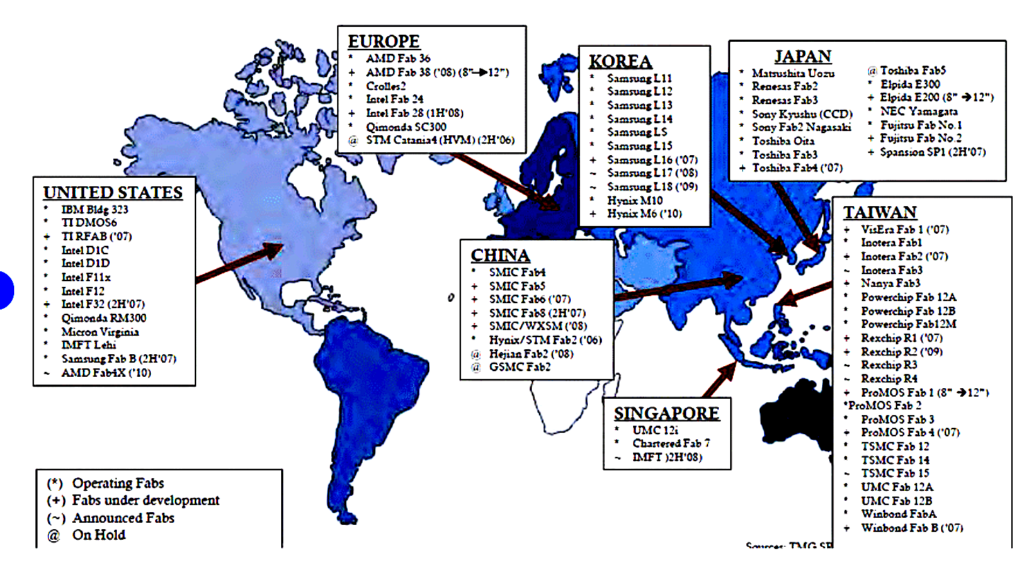
However, some experts argue that this latest move could have unintended consequences, as it may lead to increased tensions between nations and create new challenges for the global economy. The semiconductor industry is a complex and interdependent network of manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers, and any disruption in this system can have far-reaching effects. For instance, the shortage of chips in recent times has caused significant delays in the production of cars, electronics, and other critical goods. Similarly, trade disputes between nations can impact the flow of goods, causing supply chain disruptions and economic instability. Thus, these actions should be taken with caution and consideration of the potential consequences on the global economy.
I believe the imposition of chip export controls on China is a complex issue with many factors at play. While it may have short-term benefits for the US and its allies, it is important to consider the long-term implications and the delicate balance between maintaining power and ensuring stability in the global marketplace. For this seeming indiscretion, everyone expects China to respond to these countries in a way they might understand. Only time will tell if this latest move proves to be a wise strategy.







